The standard enthalpy change of electron gain, ΔHego, is the change in enthalpy when one mole of electrons is attached to atoms or anions in the gaseous state to form one mole of anions under standard conditions.
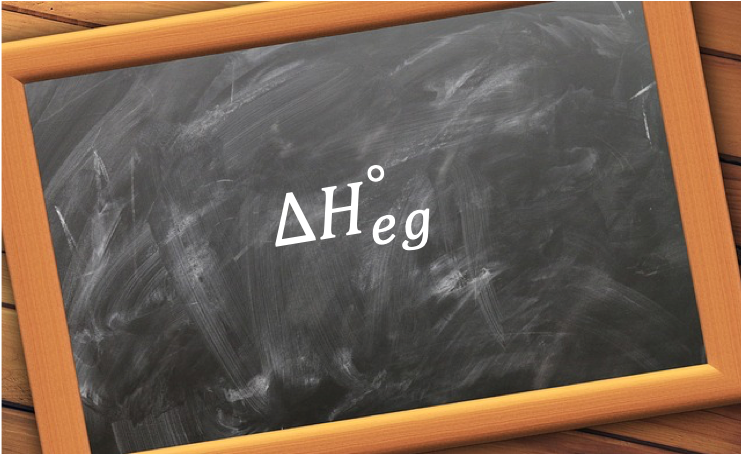
When one mole of electrons is attached to atoms to form one mole of monovalent anions, the change in enthalpy is called the first electron gain enthalpy, e.g.
When one mole of electrons is attached to monovalent anions to form one mole of divalent anions, the change in enthalpy is called the second electron gain enthalpy, e.g.
The standard enthalpy change of electron gain of a substance is calculated from the substance’s electron affinity (the two are not the same, as electron affinity is defined at absolute zero) using Kirchhoff’s law, or from the relationship:
which states that the standard enthalpy change of electron gain of a species is the negative of the standard enthalpy change of ionisation of that species with an additional electron attached, e.g.
Substituting eq3 from the previous section in eq5,
Electron affinities are determined experimentally using photoelectron spectroscopy (PES) where the known energy of an incident photon on an anion equals to the atom’s electron affinity plus the measured kinetic energy of the ionised electron. These electron affinities are then converted to electron affinities at absolute zero, which are then converted to standard enthalpies of electron gain, with both conversions using Kirchhoff’s law. It is easier to measure ionisation energies than electron affinities and therefore standard enthalpies of electron gain of substances are usually calculated using eq4.