To analyse paper chromatography results, we determine the retention factor, Rf, where
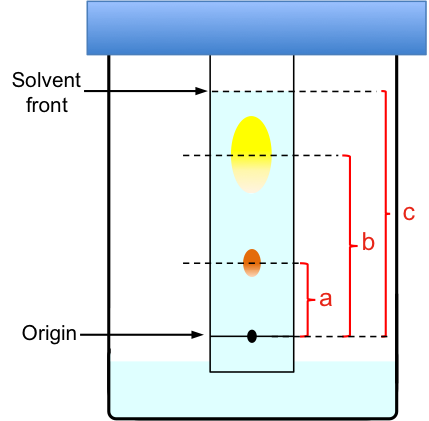
For example (with reference to the above diagram),
Question
-
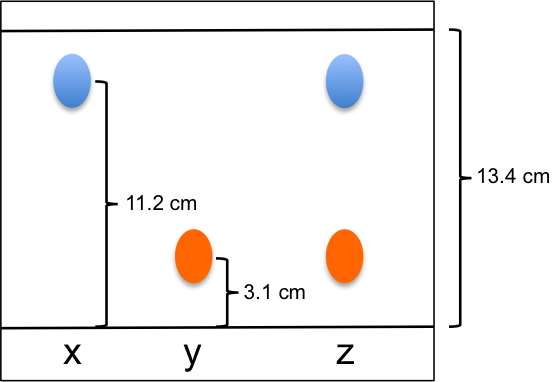
- Based on the diagram below, what are the Rf values for samples x and y?
- With reference to the calculated Rf values, describe the likely solubilities of samples x and y in the mobile and/or stationary phases.
- What could be the composition of sample z?
Answer
-
- Rf,x = 11.2/13.4 = 0.84; Rf,y = 3.1/13.4 = 0.23
- Since Rf,x > Rf,y , sample x is relatively more soluble in the mobile phase than sample y (or sample y is relatively more soluble in the stationary phase than sample x), assuming partitioning is the main mechanism of separation.
- Sample z could be a mixture of x and y.