A state function is a mathematical function that describes the thermodynamic state of a system at equilibrium.
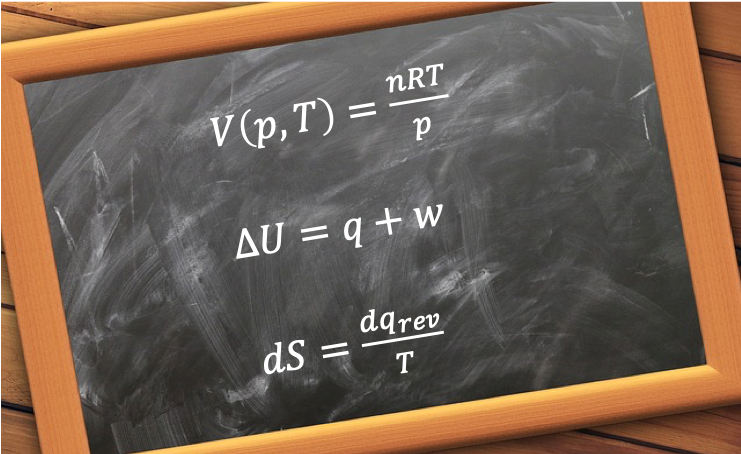
The ideal gas equation is a state function because it describes the state of a gas at equilibrium with a specific set of values: volume, temperature and pressure. In other words, a state function for a system at equilibrium relates one or more input thermodynamic properties to an output thermodynamic property.
Since a particular state of a system at equilibrium is characterised by a set of numbers, the output value of a state function for that state is independent on the path (i.e. process) taken to reach that value.
Question
Show that the output of the state function is independent on the path taken to reach it.
Answer
The total differential of is
The second cross partial derivatives of is
and
Eq19 refers to the path where the function V is changed with respect T at constant p, followed by a change with respect to p at constant T, whereas eq20 refers to another path where the function V is changed with respect to p at constant T, followed by a change with respect to T at constant p. If eq19 is equal to eq20, the change of V is independent of the path taken. Substituting in eq19 and eq20 gives
for both equations. Therefore, the change of V is path-independent and the differential given by eq18 is called an exact differential.
Finally, if the output value of the function of pressure and the output value of the function of volume are path-independent, then the output value of the product of the two functions or the output value of the sum of the two functions are also path-independent.
