How do we construct and balance redox equations?
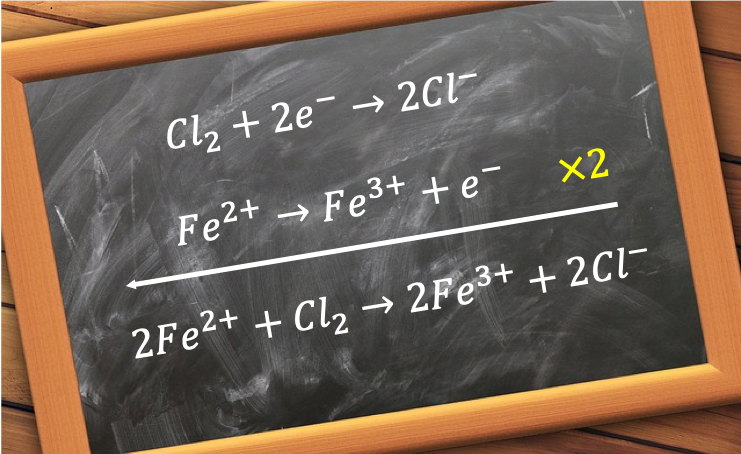
The way to construct a redox equation is to write two balanced ionic half-reaction equations, one for the oxidising agent and the other one for the reducing agent, and combine them. The method to balance each half-reaction equation is slightly different from that of a normal stoichiometric equation and involves the following steps:-
-
- Balance elements other than O and H
- Balance O by adding H2O
- Balance H by adding H+
- Balance excess positive charges by adding electrons, e–
- (For reaction in a basic solution) Balance H+ by adding OH– to both sides, then combine H+ and OH– to form H2O and cancel out any common terms
For example, the redox equation for the oxidation of acidified iron (II) sulphate by potassium dichromate (VI) is constructed as follows:
1st half-reaction equation
Fe2+ → Fe3+
Balancing the equation
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e– eq1
(note that steps 1 through 3 and step 5 do not apply)
2nd half-reaction equation
Cr2O72- → Cr3+
Balancing the equation
Cr2O72- → 2Cr3+
Cr2O72- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Cr2O72- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 6e–→ 2Cr3+ + 7H2O eq2
(note that step 5 does not apply)
Next, combine the balanced half-reaction equations, cancel any common terms and ensure that all electrons are eliminated in the final equation. For this example, we multiply eq1 by 6 throughout before adding to eq2, giving:
6Fe2+(aq) + Cr2O72- (aq) + 14H+ (aq) → 6Fe3+(aq) + 2Cr3+ (aq) + 7H2O (l)
Question
Write the redox equation for the oxidation of sodium formate by potassium manganite (VII) to form sodium carbonate and manganese dioxide in slightly basic conditions.
Answer
1st half-reaction equation
HCO2– → CO32-
Balancing the equation
HCO2– + H2O → CO32-
HCO2– + H2O → CO32- + 3H+
HCO2– + H2O → CO32- + 3H+ + 2e–
HCO2– + H2O + 3OH– → CO32- + 3H+ + 2e–+ 3OH–
HCO2– + H2O + 3OH– → CO32- + 3H2O + 2e–
HCO2– + 3OH– → CO32- + 2H2O + 2e–
2nd half-reaction equation
MnO4– → MnO2
Balancing the equation
MnO4– → MnO2 + 2H2O
MnO4– + 4H+ → MnO2 + 2H2O
MnO4– + 4H+ + 3e– → MnO2 + 2H2O
MnO4– + 4H+ + 3e– + 4OH– → MnO2 + 2H2O + 4OH–
MnO4– + 4H2O + 3e– → MnO2 + 2H2O + 4OH–
MnO4– + 2H2O + 3e– → MnO2 + 4OH–
Combining the balanced half-reaction equations, we have,
3HCO2– (aq) + OH– (aq) + 2MnO4– (aq) → 3CO32- (aq) + 2MnO2 (s) + 2H2O (l)