A disproportionation reaction is one in which an atom in a reactant undergoes both oxidation and reduction. For example,
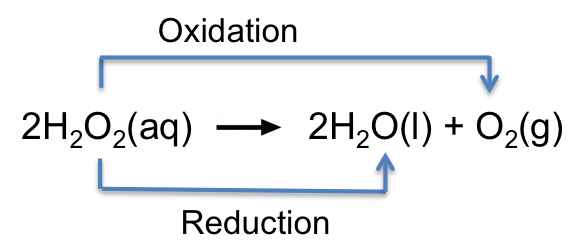
The O in H2O2 (oxidation state of O = -1) is oxidised to the O in O2 (oxidation state of O = 0) and reduced to the O in H2O (oxidation state of O = -2).
A disproportionation reaction happens when the oxidation state of an element in a compound is unstable and can achieve greater stability by splitting into two species — one at a higher oxidation state and one at a lower. This is often driven by the products having a lower total Gibbs energy than the reactant. It may also occur due to favourable changes in enthalpy and entropy.
