The overlap integral is a measure of the extent of overlap of an orbital
of an atom
with the orbital
of another atom
.
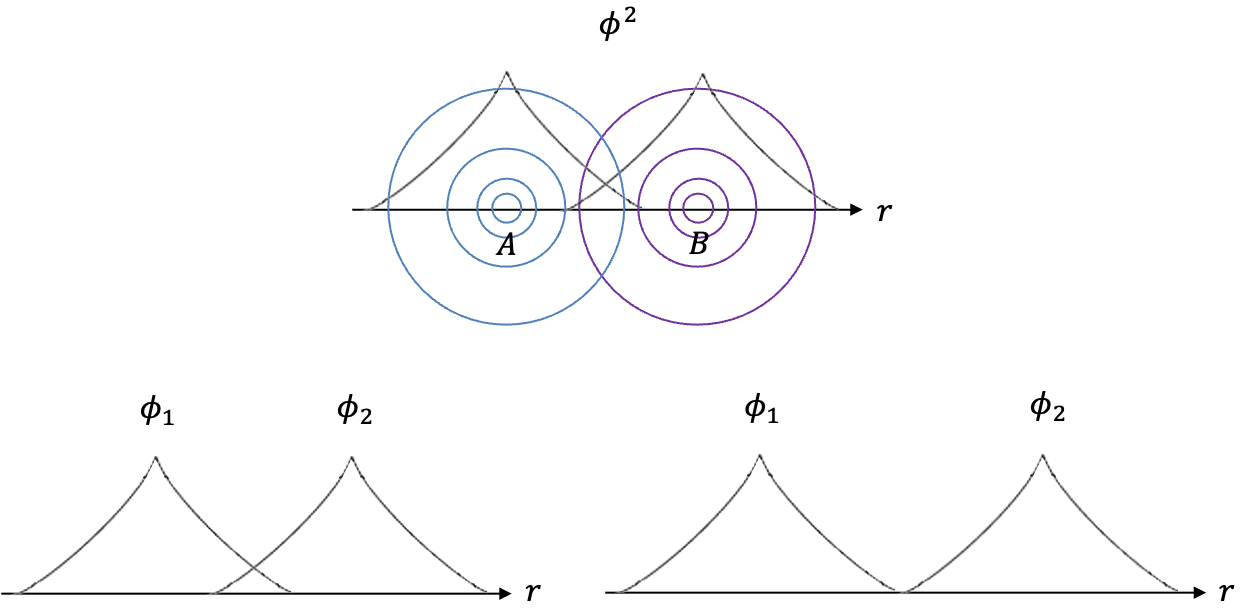
The diagram above depicts the graphs of and
for points along the internuclear axis
of two
orbitals. With regard to the two graphs of
,
is the continuous sum of the product of the wavefunctions
and
at each
.
if the wavefunctions overlap and
if the wavefunctions do not overlap. This implies that if
, bonding does not occur between the atoms because the orbitals of the two atoms are too far apart. Therefore,
not only provides a quantitative measure of the extent of overlap of an orbital
of an atom
with the orbital
of another atom
, but an indication of whether bonding is possible.
Group theory is often employed to determine if the overlap integral between two wavefunctions is necessarily zero without having to compute the integral algebraically.
