2-dimensional paper chromatography is a paper chromatographic technique where a chromatogram is first developed using a particular solvent (via either ascending or descending paper chromatography) and then rotated by 90 degrees for a second run with another solvent.
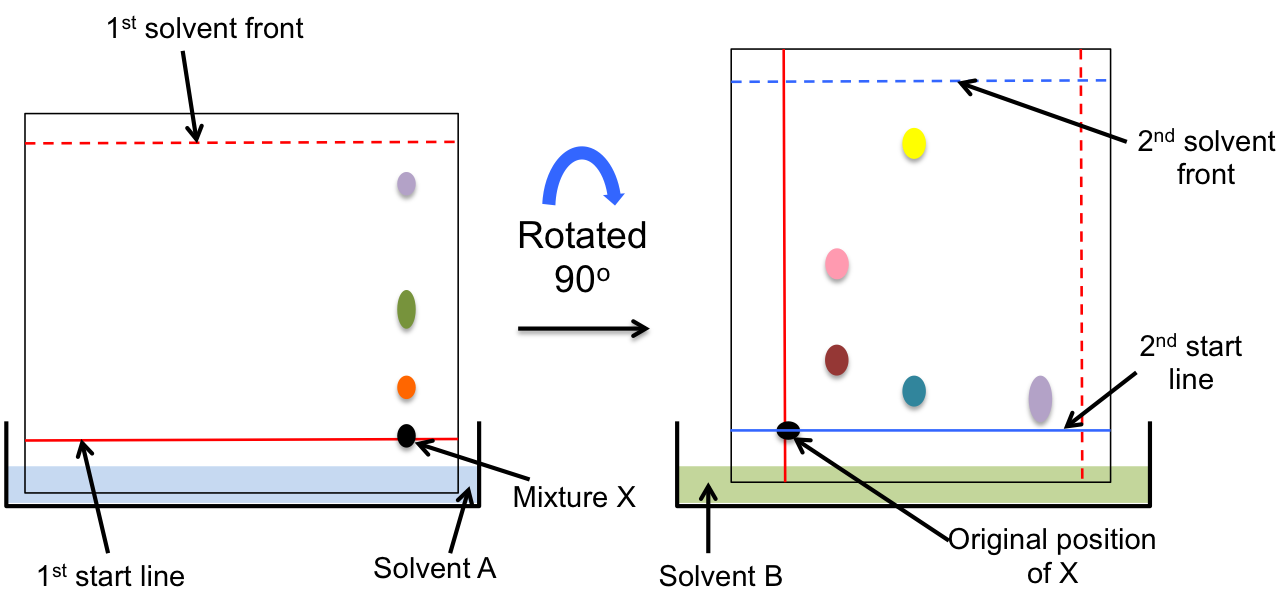
2-dimensional paper chromatography allows components that are not separated by the first solvent (due to the components being insoluble in the solvent) to be parted by the second solvent, and hence produces a chromatogram with a better ‘resolution’ than a 1-dimensional paper chromatogram.
Question
With reference to the above diagram, what is the minimum number of chemical components in mixture X?
Answer
5