Paper chromatography is an analytical technique used for separating and identifying components of a mixture. The most common form of paper chromatography is ascending paper chromatography, which involves applying a small drop of a solution mixture to a piece of filter paper a short distance from one end. After drying the drop of solution, the paper is suspended in a container, with the same end of the paper dipped in a solvent without immersing the drop itself.
The mixture is separated as the solvent flows up the paper by capillary action, moving the components of the mixture at different rates. The diagram below shows a drop of black ink being separated into its coloured components.
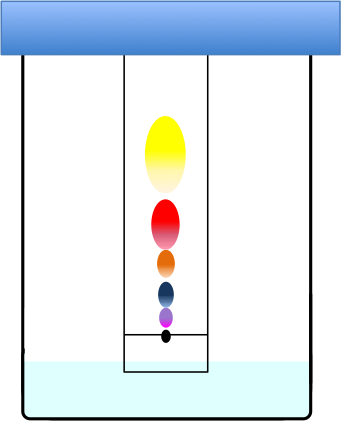
Examples of other forms of paper chromatography are descending chromatography and radial chromatography.