What is the formula of the titration curve of a triprotic acid versus a strong base?
Consider a solution containing water, a triprotic acid of concentration Ca and a strong base of concentration Cb with the following equilibria:
With reference to charge balance of the above equilibria, the sum of the number of moles of cations H+ and B+ must equal to that of anions H2A–, HA2-, A3- and OH–. As the volume is of the solution is common to all ions,
Read this article to understand how to arrive at eq23.
With reference to eq20, eq21 and eq22, at any point of the titration, the sum of the number of moles of H3A, H2A–, HA2- and A3– must equal to the number of moles of H3A if it were undissociated. As the change in volume of the solution is common to all ions,
where Va and Vb are the volume of triprotic acid in the solution and the volume of strong monoprotic base in the solution respectively. The equilibrium constant equations of eq20, eq21 and eq22 are:
Substitute eq24c in eq24b
Substitute eq25 in eq24a
Substitute eq26, eq25 and eq24c in eq24 and rearranging,
Substitute eq23 in eq24a and eq24b
Substitute eq7, eq27, eq28, eq29, Kw = [H+][OH–] and [H+] = 10-pH in eq23,
where
Eq30 is the complete pH titration curve for a triprotic acid (either strong or weak) versus monoprotic strong base system. We can input it in a mathematical software to generate a curve of pH against Vb. For example, if we titrate 10 cm3 of 0.200 M of H3PO4 (Ka1 = 7.11 x 10-3, Ka2 = 6.00 x 10-8 , Ka3 = 4.80 x 10-13 ) with 0.100 M of NaOH, we have the following:
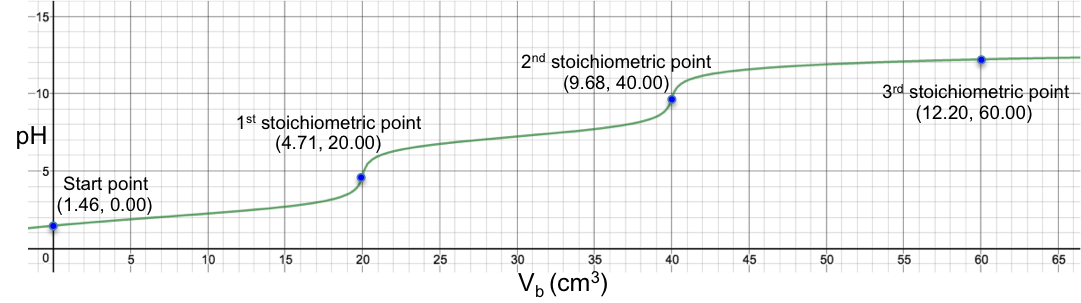
The 1st and 2nd stoichiometric points are titrated using methyl orange and thymolphthalein as indicators respectively, while the 3rd stoichiometric point is non-discernible. Another way to titrate phosphoric acid is to first react it with excess cation to completely precipitate the phosphate salt, thereby releasing all H+, which is then titrated with a strong base:
