The time-dependent perturbation theory is a method for finding an approximate solution to a problem that is characterised by the time-varying properties of a quantum mechanical system. For example, the electronic state of a molecule exposed to electromagnetic radiation is constantly perturbed by the oscillating electromagnetic field. Time-dependent perturbation theory is key to finding solutions to such problems, and is used to calculate transition probabilities in spectroscopy.
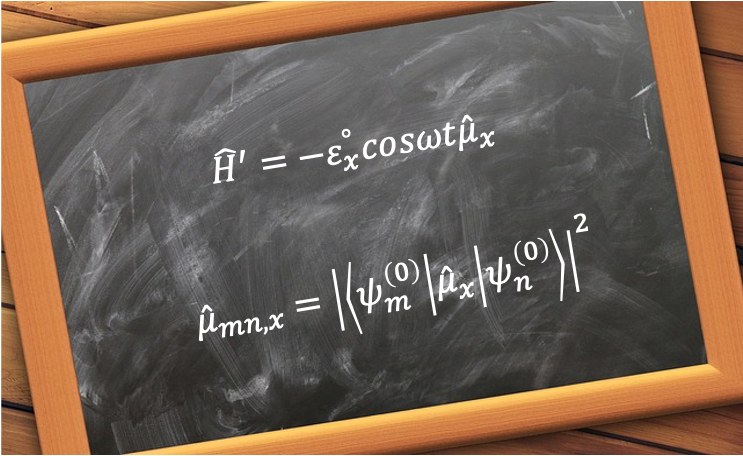
Consider the unperturbed eigenvalue equation given by eq262, where
is the unperturbed Hamiltonian,
is a complete set of orthonormal eigenfunctions of
in a Hilbert space, and
represents the exact eigenvalue solutions. Furthermore, let’s rewrite eq57 as
where
is the solution of the time-dependent Schrodinger equation. If it describes a stationary state, then
Otherwise, can be expressed generally as the linear combination
, which is also a solution of eq281a.
In the presence of radiation, we add a correction term to the Hamiltonian in eq281a:
where is the perturbed wavefunction.
Since belong to the same Hilbert space, which is spanned by
, we can express
as
where the coefficient is now a function of time because we expect
, which is the probability that a measurement of a system will yield an eigenvalue associated with
, to change with time since the Hamiltonian is now time-dependent.
Question
Show that .
Answer
Using ,
If we assume that the perturbation was turned on at time
, then the system before
is characterised by a stationary state. Substituting
in eq281d, we have
, which must be equal to eq281b at
. This implies that
Substituting eq281d in eq281c and using the unperturbed eigenvalue equation, we get
Multiplying the above equation by , integrating over all space and using
, we have
Assuming that the variation of is insignificant because the perturbation is small and over a short time from
to
, then
. Substituting eq281e in eq281f, we have
Integrating the above equation from to
and using eq281e,
Eq281g, when substituted in eq281d, gives the approximate perturbed wavefunction at
:
where is the probability that a measurement of a system will yield an eigenvalue associated with
after perturbation at
.
Let’s suppose the perturbation on an atom or molecule is caused by a plane-polarised electromagnetic wave with an electric component oscillating in the
-direction. According to classical physics, the force
on a charge
on the atom or molecule is
. It is also the negative gradient of potential energy
of interaction between the field and the charge, i.e.
. Therefore,
, whose integrated form is
, which is consistent with the classical interaction energy between the electric field and a charged particle. If we consider multiple charges and an oscillating electric field, the perturbation can be expressed approximately as
where is the maximum amplitude of the electric field in the
-direction,
is the angular frequency of the electric field and
is the operator for the
-component of the atom or molecule’s electric dipole moment, i.e.
.

Question
Why did we not consider the magnetic component of the electromagnetic wave?
Answer
This is because interaction between the magnetic component of the electromagnetic wave and the charges of an atom or molecule is more than a hundred times weaker than interaction between the electric component of the electromagnetic wave and the charges of the atom or molecule.
Substituting eq281h, and
in eq281g for
,
Since is a function of time and not position, it is a constant with regard to the integral with respect to position and we have
When , we have
, which implies that
corresponds to the transition frequency of an atom or molecule from state
to
. Therefore,
is the probability that a measurement of a system will yield an eigenvalue associated with
after perturbation at
from the state
at
(see Q&A below for how to evaluate
when
,). In other words, the transition probability from state
to
of an atom or molecule irradiated by an electromagnetic wave oscillating in the
-direction is proportional to
, which is denoted by
.

Question
Evaluate when
.
Answer
Let , with
. As
, we have
. Using L’Hopital‘s rule,
So, and grows linearly with
.
For , where
, the magnitude of the numerator is:
Therefore, the magnitude of the numerator is always between 0 and 2, which makes .
For an electromagnetic wave that is not plane-polarised, and
. We called
the transition dipole moment. In general, transitions are allowed when
, while transitions are forbidden when
.